

An overview of fiber-shaped batteries with a focus on multifunctionality, scalability, and technical difficulties. Recent advances in 1D stretchable electrodes and devices for textile and wearable electronics: materials, fabrications, and applications. Enabling deformable and stretchable batteries. We show that fibre lithium-ion batteries woven into safe and washable textiles by industrial rapier loom can wirelessly charge a cell phone or power a health management jacket integrated with fibre sensors and a textile display. Over 80 per cent capacity can be maintained after bending the fibre for 100,000 cycles. Its capacity retention reaches 90.5% after 500 charge–discharge cycles and 93% at 1C rate (compared with 0.1C rate capacity), which is comparable to commercial batteries such as pouch cells. Our mass-produced fibre batteries have an energy density of 85.69 watt hour per kilogram (typical values 8 are less than 1 watt hour per kilogram), based on the total weight of a lithium cobalt oxide /graphite full battery, including packaging. We are able to produce metres of high-performing fibre lithium-ion batteries through an optimized scalable industrial process. Systematic studies confirm that this unexpected result is true for different fibre batteries. Here we show that the internal resistance of such fibres has a hyperbolic cotangent function relationship with fibre length, where it first decreases before levelling off as length increases. However, they are difficult to produce in lengths of more than a few centimetres, and longer fibres were thought to have higher internal resistances 3, 5 that compromised electrochemical performance 6, 7.

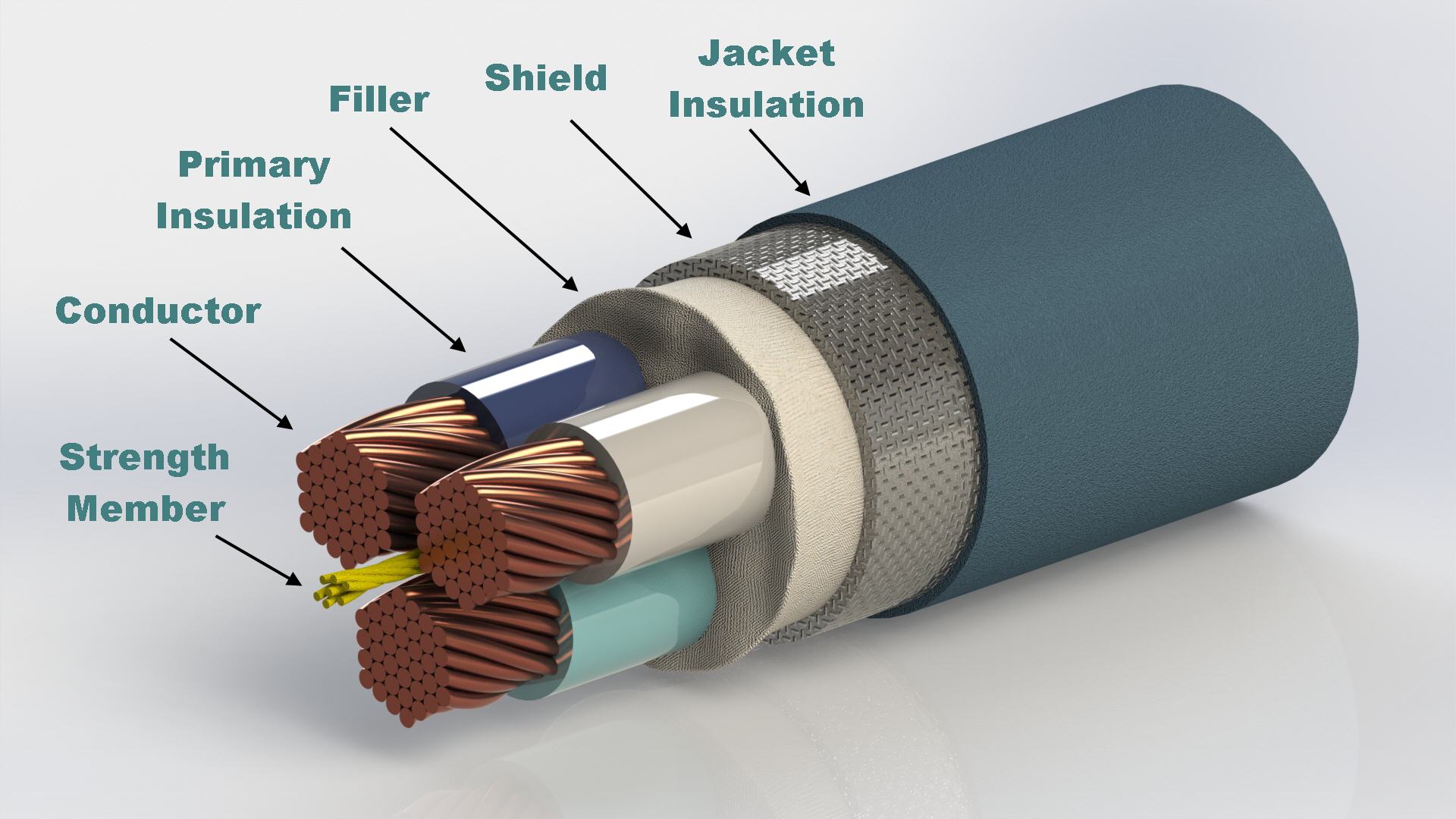
Fibre lithium-ion batteries are attractive as flexible power solutions because they can be woven into textiles, offering a convenient way to power future wearable electronics 1, 2, 3, 4.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
